What is L-Glutamine?
L-glutamine, or simply Glutamine, is an amino acid. Amino acids are a group of nutrients that aid in creating protein in the human body to supply nutritional purposes. They are present in high-protein food items, including animals and plants. Protein, for its part, is a crucial essential nutrient to maintain a healthy well-being.
L-glutamine is one of the 20 essential and non-essential amino acids that make proteins. Essential amino acids can be consumed through food sources, while non-essential ones, such as L-glutamine, are made by your body. Under normal circumstances, the body produces enough L-glutamine for most of its requirements.
Recent studies have shown that Glutamine, an amino acid, can improve the health of your gut by enhancing the microbiome of the gut as well as the mucosal barrier of the gut in its integrity, as well as by modulating inflammation responses. In turn, when it is modulated through and controlled by the vagus nerve and its Enteric Nervous System in the gut, the gut-brain link can affect the brain’s neurochemical environment.
Inadequate gut health can affect the equilibrium of neurotransmitters and cause neuropsychiatric disorders like depression. Glutamine supplementation can supplement nutritional therapy in cases of depression by promoting gut health and functioning.
When to Take L-Glutamine for Gut Health?
It is recommended to consume L-glutamine approximately 10-15 minutes before meals when you are not hungry. I recommend taking L-glutamine 3 times daily (between 3 meals daily). It is better to take it sooner than later, so try as best as you can. You should take L-glutamine if you have a gut issue such as leaky gut and IBS.
What’s “Leaky Gut?”
The human digestive tract is a complicated system that breaks down food to separate nutrients the body needs from any substance that must be eliminated.
Alongside this important role, in addition to this, the interior walls serve as a barrier to the bloodstream and organs. Although the intestine appears solid, it is permeable and comprises tiny spaces known as “tight junctions” (specialized areas that remain wide between cells’ membranes). Although these spaces keep harmful substances from getting into the bloodstream, they are why water and nutrients can enter the body.
The tight junctions aren’t open spaces with ridges. For example, research has revealed that these junctions could be loosened after eating to permit more excellent nutrient absorption. These movable spaces may also get affected due to other factors such as bowel irritation, stress, and non-nutrient-rich eating habits (fast foods). These forces could cause over-loosening, increasing the possibility of harmful material escaping from the colon.
The release of this substance from the intestine and into the body is known as “leaky gut” or intestinal hyper-permeability. As these spaces grow and expand, harmful substances can freely get into the bloodstream and trigger an aggressive immune system response. This reaction can cause generalized inflammation, allergens, migraines, digestive problems, skin irritations like acne and eczema, constipation, Rheumatoid Arthritis, chronic fatigue, hormonal imbalances, autism, fibromyalgia, and much more.
Treatment of Leaky Gut with Glutamine
Leaky gut can manifest in many different illnesses, and the diagnosis can be difficult; it is difficult to pinpoint the condition as a primary cause. A segment of the medical profession also does not recognize “leaky gut” as a medical diagnosis. Still, they agree that some chronic diseases have a problem with hyper intestinal permeability and should be treated.
To comprehend the role of Glutamine in treating leaky gut, you must first understand the basics of amino acids and proteins. The body requires proteins for healthy tissue growth, composed of 20 amino acids that each serve various functions within the body. Glutamine is among these amino acids, and research studies have proven that it has the most significant benefit in strengthening and repairing an intestinal liner.
What Can Glutamine Supplements Do?
According to a research study published in The International Journal of Molecular Sciences In gut physiology, Glutamine promotes enterocyte proliferation, regulates tight junction proteins, and suppresses pro-inflammatory signaling pathways.
Since glutamine stores deplete in extreme metabolic stress, such as sepsis, trauma, and intestinal inflammation, the supplementation of Glutamine has been studied in patients to enhance their clinical outcomes.
Naturally occurring Glutamine within the body is used to safeguard the intestine. It is only natural that a supplement will help to improve intestinal stability. When the lining of your intestine is healthy, it will significantly reduce inflammation in your body. This could, in turn, give your immune system the chance to heal.
Which Glutamine Supplement Should You Select?
If you’re looking to increase your intake of Glutamine through only diet, it is essential to realize that this will not be straightforward. When you consume food that contains Glutamine, it competes with all the amino acids that these food items have, which means that the amount you absorb is not enough to build up the intestinal wall. Fortunately, for those who require the most effective intestinal support, pure glutamine supplements exist.
When selecting a supplement, I strongly suggest speaking with your physician to decide which one is best for you. You can choose the dosage when you’ve decided which supplement to take.
For general use, you can go through this maintenance protocol for L-Glutamine that was developed in collaboration with the Food and Drug Administration. I suggest the following maintenance plan for my patients because of its simplicity and effectiveness: Take 10-15 grams of L-Glutamine 100% powder mixed with 8 ounces of water daily and night for two weeks.
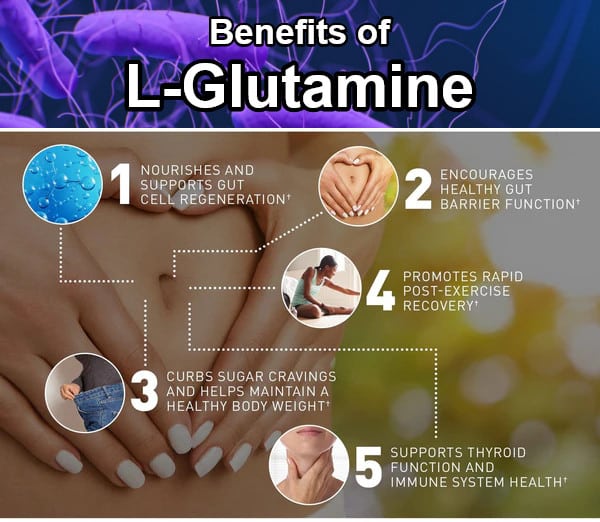
Can L-Glutamine Be Used to Treat IBS?
L-glutamine could help in the treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). The intestine’s tissues use this amino acid as a source of fuel to function correctly. L-glutamine also plays a vital role in maintaining the proper barrier structures within the intestine.
IBS is among the most frequent intestinal conditions.
IBS Symptoms
IBS symptoms can be described as IBS could be:
- Bloating
- constipation
- cramping
- diarrhea
- general irregularity
- persistent stomach upset
- Mucus white in the stool
L-glutamine can help those who suffer from these symptoms frequently or have been diagnosed with IBS. In some instances, it is thought that IBS itself may be the result of an L-glutamine shortage.
L-Glutamine deficiencies can occur for many causes:
- shock
- trauma
- serious infections
- vigorous exercise
- radiation treatment
- chemotherapy
- significant stress
Consuming too much L-glutamine can reduce your levels. In some rarer cases, this could be caused by an immune disorder such as HIV or AIDS.
L-glutamine is produced naturally by the body. It can be consumed in the form of powder or supplements available in stores or through prescription. In addition, it can be absorbed through diet.
Food Sources of L-Glutamine
Food sources that contain Glutamine include:
- chicken
- Fish
- dairy
- Tofu
- cabbage
- spinach
- beets
- peas
- lentils
- beans
A direct intake of L-glutamine could be suggested to address any deficiencies, especially during stress or severe disease.
Consult your physician about L-glutamine, a potential treatment to treat your IBS problems. L-glutamine could aid if you suspect you have a health issue or other problems and suffer from IBS.
Read More:
Biotics 8 Review: SCAM or A Legit Probiotic for Men?
L-Glutamine Deficiency
The most common reasons why people may be suffering from L-glutamine deficiency include:
- Extreme stress
- trauma
- serious infections
- intense exercise
- radiotherapy
- chemotherapy
- Immune disorders, for instance, HIV as well AIDS
- chronic gastrointestinal disorders, such as Crohn’s disease, eosinophilic gastric ulcer (EoE), or inflammatory bowel disease
- absence of L-glutamine from the diet
L-glutamine aids people suffering from IBS by helping protect the mucous membranes of the esophagus and the intestines.
L-glutamine is also a great way to boost the activity of immune cells within the gut, helping to prevent infections and inflammation and relaxing the intestinal tissue. Since L-glutamine is utilized to produce energy, it may aid in the decrease of intestinal spasms.
People suffering from stress-related IBS might also notice that taking more L-glutamine helps ease the symptoms. This advantage is due to the body’s release of cortisol whenever stressed, which may lower the levels of L-glutamine accumulated in muscles.
Research about the Treatment of IBS by L-Glutamine
There are none of the studies or studies have proved that L-glutamine can improve IBS. One study by the government was initially proposed in 2010, but it was not finished. Other studies touch on the issue but are old and not relevant anymore.
The concept that L-glutamine helps with IBS is mentioned in a recent review. The research reviewed concluded that L-glutamine can improve the gut’s permeability. This prevents unwanted toxins from in the digestive tract.
It is believed that IBS itself may be caused by the inability of the gut to permeabilize and is particularly prevalent in people with diarrhea. IBS. This suggests that L-glutamine may be a potential remedy for IBS; however, further research is required to confirm this.
Frequently Asked Questions about L-Glutamine and Gut Health
What Should I Be Looking Out for Taking L-Glutamine?
The consensus is that taking L-glutamine is generally safe. Be sure to adhere to the doses recommended, however. In excess, it could be harmful to your health.
For IBS, The dosage the doctor recommends depends on the specifics of your case. The usual dosage is 30 grams daily. It is divided into five grams and taken six times daily.
A variety of side effects can occur if you’re allergic or sensitive to L-glutamine or consume too many. Some products include nausea, vomiting, joint pain, and hives.
If any of these or other adverse reactions develop, get medical attention immediately.
Studies have shown that specific cancer cells multiply rapidly when exposed to L-glutamine.
The tumor cells consume L-glutamine as a preferred source of fuel. This is why it’s recommended for people who have cancer or are at risk of developing cancer to avoid taking supplements. Further studies are needed to determine how L-glutamine and specific cancers interact.
What is the best time to take Glutamine to improve my stomach?
Ideally, it’s best to consume L-glutamine within 10-15 minutes before meals when you are not hungry, and I generally suggest taking L-glutamine 3 times a day (between three meals every day). It is better to start taking it earlier than later, so do your best.
When should I consume Glutamine in the morning or at night?
It is suggested that you consume 5 grams of Glutamine per dose at these times. Before bed, take five grams of Glutamine before bedtime to ensure you are ready to sleep. Numerous studies suggest that taking glutamine supplements before rest increases growth hormone levels when you sleep.
Do I have to take L-glutamine before or after eating?
Do you need to take l-glutamine in conjunction when you eat? No. The best way to absorb amino acids is to supplement them on an empty stomach. Also, avoid taking it during meals or snacks.
How much L-glutamine do I need to take to heal my digestive tract?
We recommend this maintenance plan for its simplicity and effectiveness for my patients. Take between 10 and 15g of pure L-Glutamine powder mixed with 8 ounces of water in the morning and at night for 2 weeks.
How long will it take for L-glutamine to reach the digestive tract?
Studies conducted for children and adults have shown that supplementing with L-glutamine is effective in helping to strengthen the gut lining within less than 10 days, which is a significant improvement for those who suffer from leaky gut.
Can L-glutamine assist with digestive problems?
The reviewed studies found that L-glutamine can improve intestinally or gut permeability. This prevents unwanted toxins from that enter the digestive tract.
Which are the adverse side effects of L-glutamine?
Although it is not common, large amounts of Glutamine could cause adverse effects that require medical attention, such as urine, blood, changes in skin color, and lower back pain: rapid heartbeat, dizziness, or a rash. Introducing a supplement made from Glutamine to your diet could cause minor negative effects.
When is the ideal time to consume L-glutamine?
It is recommended to consume L-glutamine approximately 10-15 minutes before eating and with an empty stomach. I recommend taking L-glutamine 3 times daily (between 3 meals daily). It is better to start taking it earlier than later, so do your best.
Lactobacillus acidophilus, a probiotic bacteria commonly found in yogurt, is also suitable for your digestive system. Research has proven that it is effective in treating and preventing infections and reducing the negative effects of digestion that antibiotics can cause.
Read More:
Best Magnesium for Gut Health: 13 Types of Magnesium Discussed Here!
Are Tomatoes A Good Probiotic? 3 Facts You Should Know
Best Over the Counter Probiotic for Gut Health: Easy Guide 2022
Best Probiotic for Gut Health and Weight Loss: An Ultimate Guide 2022
Best Probiotic for Vaginal and Gut Health: The Best Guide 2022
Scientific Studies and References
- MedicalNewsToday
- WebMD
- National Library of Medicine
- PubMed.gov
- European Journal of Clinical Nutrition
-
Rao R, Samak G. Role of Glutamine in Protection of Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junctions. J Epithel Biol Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;5(Suppl 1-M7):47-54. doi: 10.2174/1875044301205010047. PMID: 25810794; PMCID: PMC4369670.
- Brett J. Deters, Mir Saleem,
The role of glutamine in supporting gut health and neuropsychiatric factors,
Food Science and Human Wellness,
Volume 10, Issue 2,
2021,
Pages 149-154,
ISSN 2213-4530,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2021.02.003. -
Wang B, Wu G, Zhou Z, Dai Z, Sun Y, Ji Y, Li W, Wang W, Liu C, Han F, Wu Z. Glutamine and intestinal barrier function. Amino Acids. 2015 Oct;47(10):2143-54. doi: 10.1007/s00726-014-1773-4. Epub 2014 Jun 26. PMID: 24965526.
-
van der Hulst RR, von Meyenfeldt MF, Soeters PB. Glutamine: an essential amino acid for the gut. Nutrition. 1996 Nov-Dec;12(11-12 Suppl):S78-81. doi: 10.1016/s0899-9007(97)85206-9. PMID: 8974125.

















